Abstract
Introduction
It is claimed that bioactive coils induce accelerated and more durable aneurysm healing. Data supporting this claim are quite limited. Our purpose was to compare the angiographic and histological results obtained following treatment with different coil types.
Methods
Bifurcation type aneurysms were surgically created in 24 dogs and treated using standard clinical techniques. Eight were treated with Guglielmi detachable coils (GDC), eight with first-generation Matrix coils, and eight with a combination of GDC and Matrix coils. The aneurysms were explanted and final angiographic evaluations performed 12 weeks after treatment. Angiographic and histological outcomes were documented.
Results
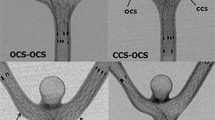
Increased coil compaction with aneurysm recurrence was found in aneurysms treated with first-generation Matrix coils as compared to standard GDC (P = 0.0001). In aneurysms treated with first-generation Matrix coils thrombus organization was better than in those treated with either standard GDC coils (P = 0.008) or with a combination of GDC and Matrix coils (P = 0.04). In aneurysms treated with first-generation Matrix coils there were no endothelialized vascular clefts within the coil mass, but they were seen in the majority of aneurysms treated with GDC or a combination of GDC and Matrix coils (P = 0.003).
Conclusion
Aneurysms treated with first-generation Matrix coils showed the greatest degree of coil compaction and aneurysm recurrence on the final angiographic evaluation. Aneurysms treated with first-generation Matrix coils showed enhanced thrombus organization and absence of vascular clefts at the aneurysm neck that were markedly different from those treated with bare platinum coils or a combination of GDC and Matrix coils.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Panel comprised of physician consultants to Boston Scientific Neurovascular.
References
Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, Sandercock P, Clarke M, Shrimpton J, Holman R; International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) Collaboration Group (2002) International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet 360(9342):1267–1274
Raymond J, Guilbert F, Weill A, Georganos SA, Juravsky L, Lambert A, Lamoureux J, Chagnon M, Roy D (2003) Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke 34(6):1398–1403
Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Mawad M (1997) Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of acute intracranial aneurysm: perioperative anatomical and clinical outcome in 403 patients. J Neurosurg 86:475–482
Fernandez Zubillaga A, Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Duckwiler GR (1994) Endovascular occlusion of intracranial aneurysms with electrically detachable coils: correlation of aneurysm neck size and treatment results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:815–820
Malisch TW, Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Gobin YP, Martin NA, Frazee JG (1997) Intracranial aneurysms treated with the Guglielmi detachable coil: midterm clinical results in a consecutive series of 100 patients. J Neurosurg 87:176–183
Bavinzski G, Talazoglu V, Killer M, Richling B, Gruber A, Gross CE, Plenk H Jr (1999) Gross and microscopic histopathological findings in aneurysms of the human brain treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. J Neurosurg 91:284–293
Szikora I, Seifert P, Hanzely Z, Kulcsar Z, Berentei Z, Marosfoi M, Czirjak S, Vajda J, Nyary I (2006) Histopathologic evaluation of aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils or Matrix detachable microcoils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27(2):283–288
Ding YH, Dai D, Lewis DA, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF (2005) Angiographic and histologic analysis of experimental aneurysms embolized with platinum coils, Matrix and HydroCoil. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1757–1763
Raymond J, Guilbert F, Metcalfe A, Gevry G, Salazkin I, Robledo O (2004) Role of the endothelial lining in recurrences after coil embolization: prevention of recanalization by endothelial denudation. Stroke 35(6):1471–1475
Mawad ME, Mawad JK, Cartwright J, Gokaslan Z (1995) Long-term histopathological changes in canine aneurysms embolized with Guglielmi detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:7–13
Reul J, Weis J, Spetzger U, Konert T, Fricke C, Thron A (1997) Long-term angiographic and histopathologic findings in experimental aneurysms of the carotid bifurcation embolized with platinum and tungsten coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:35–42
Raymond J, Leblanc P, Morel F, Salazkin I, Gevry G, Roorda S (2003) Beta radiation and inhibition of recanalization after coil embolization of canine arteries and experimental aneurysms: how should radiation be delivered? Stroke 34(5):1262–1268
Ahuja AA, Hergenrother RW, Strother CM, Rappe AA, Cooper SL, Graves VB (1993) Platinum coil coatings to increase thrombogenicity: a preliminary study in rabbits. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:794–798
Szikora I, Wakhloo AK, Guterman LR, Chavis TD, Dawson RC 3rd, Hergenrother RW, Twyford RH, Hopkins LN (1997) Initial experience with collagen-filled Guglielmi detachable coils for endovascular treatment of experimental aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:667–672
Dawson RC, Krisht AF, Barrow DL, Joseph GJ, Shengelaia GG, Bonner G (1995) Treatment of experimental aneurysms using collagen-coated microcoils. Neurosurgery 36:133–140
Kallmes DF, Williams AD, Cloft HJ, Lopes MBS, Hankins GR, Helm GA (1998) Platinum coil-mediated implantation of growth factor-secreting endovascular tissue grafts: an in vivo study. Radiology 207:519–523
Venne D, Raymond J, Allas S, Roy D, Leclerc G, Boushria M, Brazeau P (1999) Healing of experimental aneurysms. II: Platelet extracts can increase the thickness of the neointima at the neck of treated aneurysms. J Neuroradiol 26:92–100
Murayama Y, Vinuela F, Suzuki Y, Do HM, Massoud TF, Guglielmi G, Ji C, Iwaki M, Kusakabe M, Kamio M, Abe T (1997) Ion implantation and protein coating of detachable coils for endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms: concepts and preliminary results in a swine model. Neurosurgery 40:1233–1244
Murayama Y, Vinuela F, Suzuki Y, Akiba Y, Ulihoa A, Duckwiler GR, Gobin YP, Vinters HV, Iwaki M, Abe T (1999) Development of the biologically active Guglielmi detachable coil for the treatment of cerebral aneurysms. Part II: an experimental study in a swine aneurysm model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1992–1999
de Gast AN, Altes TA, Marx WF, Do HM, Helm GA, Kallmes DF (2001) Transforming growth factor beta-coated platinum coils for endovascular treatment of aneurysms: an animal study. Neurosurgery 49(3):690–694
Dai D, Ding YH, Danielson MA (2007) Endovascular treatment of experimental aneurysms by use of fibroblast-coated platinum coils: an angiographic and histopathologic study. Stroke 38(1):170–176
German WJ, Black SPW (1954) Experimental production of carotid aneurysms. New Engl J Med 3:463–468
Raymond J, Roy D, Bojanowski M, Moumdjian R, L’Esperance G (1997) Endovascular treatment of acutely ruptured and unruptured aneurysms of the basilar bifurcation. J Neurosurg 86:211–219
Murayama Y, Nien YL, Duckwiler G, Gobin YP, Jahan R, Frazee J, Martin N, Vinuela F (2003) Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of cerebral aneurysms: 11 years’ experience. J Neurosurg 98(5):959–966
Turk AS, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Niemann DB, Consigny D, Rappe A, Grinde J, Strother CM (2007) Natural history of the canine vein pouch aneurysm model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(3):531–532
Strother CM, Graves VB, Rappe AA (1992) Aneurysm hemodynamics: an experimental model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 13:1089–1095
Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, McDougall CG (2006) Durability of aneurysm embolization with Matrix detachable coils. Neurosurgery 58(1):51–59
Niimi Y, Song J, Madrid M, Berenstein A (2006) Endosaccular treatment of intracranial aneurysms using Matrix coils: early experience and midterm follow-up. Stroke 37(4):1028–1032
Murayama Y, Tateshima S, Gonzalez NR, Vinuela F (2003) Matrix and bioabsorbable polymeric coils accelerate healing of intracranial aneurysms: long-term experimental study. Stroke 34(8):2031–2037
Linfante I, Akkawi NM, Perlow A, Andreone V, Wakhloo AK (2005) Polyglycolide/polylactide-coated platinum coils for patients with ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysms: a single-center experience. Stroke 36(9):1948–1953
Taschner CA, Leclerc X, Rachdi H, Barros AM, Pruvo JP (2005) Matrix detachable coils for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Stroke 36:2176–2180
Murayama Y, Vinuela F, Ishii A, Nien YL, Yuki I, Duckwiler G, Jahan R (2006) Initial clinical experience with Matrix detachable coils for the treatment of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 105(2):192–199
Song JK, Niimi Y, Yoshino Y, Khoyama S, Berenstein A (2007) Assessment of Matrix coils in a canine model of a large bifurcation aneurysm. Neuroradiology 49:231–235
Kai Y, Hamada J, Morioka M, Yano S, Kuratsu J (2005) Evaluation of the stability of small ruptured aneurysms with a small neck after embolization with Guglielmi detachable coils: correlation between coil packing ratio and coil compaction. Neurosurgery 56(4):785–792
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the significant contributions of Jennifer Powers and Al Rappe.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was supported by a grant from Boston Scientific Corporation. Drs. Turk and Strother are consultants for Boston Scientific Corporation. Victoria Carr-Brendel and Igor Polyakov are employees of Boston Scientific Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turk, A.S., Luty, C.M., Carr-Brendel, V. et al. Angiographic and histological comparison of canine bifurcation aneurysms treated with first generation matrix and standard GDC coils. Neuroradiology 50, 57–65 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0302-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0302-5