Abstract
Introduction
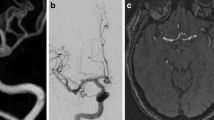
Intracranial flow diverting devices are increasingly used to treat cerebral aneurysms. A reliable, non-invasive follow-up modality would be desirable. Our aim was to compare intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography (ia DSA) to angiographic computed tomography with intravenous contrast agent application (iv ACT) in the visualisation of flow diverting devices and aneurysm lumina.
Methods
Follow-up monitoring by iv ACT (n = 36) and ia DSA (n = 25) in 14 patients treated with flow diverting devices for intracranial aneurysms was evaluated retrospectively. Images were evaluated by two neuroradiologists in anonymous consensus reading regarding the device deployment, wall apposition, neck coverage of the aneurysm, opacification of the vessel and device lumen, as well as the degree of aneurysm occlusion.
Results
Corresponding ia DSA and iv ACT images were scored identically in all patients regarding the stent deployment, wall apposition and neck coverage, as well as the degree of aneurysm occlusion and patency status of the device and parent artery. Opacification of the parent vessel lumen and perfused parts of the aneurysm was considered slightly inferior for iv ACT in comparison with ia DSA (seven of 36 cases), without impact on diagnosis.
Conclusions
We demonstrated the feasibility and diagnostic value of iv ACT in follow-up imaging of intracranial flow diverting devices. Due to its high spatial resolution and non-invasive character, this novel technique might become a valuable imaging modality in these patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sadasivan C, Lieber BB, Cesar L, Miskolczi L, Seong J, Wakhloo AK (2006) Angiographic assessment of the performance of flow diverters to treat cerebral aneurysms. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 1:3210–3213
Fiorella D, Hsu D, Woo HH, Tarr RW, Nelson PK (2010) Very late thrombosis of a pipeline embolization device construct: case report. Neurosurgery 67:313–314
Lubicz B, Collignon L, Raphaeli G, Pruvo JP, Bruneau M, De Witte O, Leclerc X (2010) Flow-diverter stent for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a prospective study in 29 patients with 34 aneurysms. Stroke 41:2247–2253
Kulcsár Z, Houdart E, Bonafé A, Parker G, Millar J, Goddard AJ, Renowden S, Gál G, Turowski B, Mitchell K, Gray F, Rodriguez M, van den Berg R, Gruber A, Desal H, Wanke I, Rüfenacht DA (2011) Intra-aneurysmal thrombosis as a possible cause of delayed aneurysm rupture after flow-diversion treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:20–25
Turowski B, Macht S, Kulcsár Z, Hänggi D, Stummer W (2011) Early fatal hemorrhage after endovascular cerebral aneurysm treatment with a flow diverter (SILK-Stent): do we need to rethink our concepts? Neuroradiology 53:37–41
Benndorf G, Strother CM, Claus B, Naeini R, Morsi H, Klucznik R, Mawad ME (2005) Angiographic CT in cerebrovascular stenting. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1813–1818
Buhk JH, Lingor P, Knauth M (2008) Angiographic CT with intravenous administration of contrast medium is a noninvasive option for follow-up after intracranial stenting. Neuroradiology 50:349–354
Struffert T, Ott S, Adamek E, Schwarz M, Engelhorn T, Kloska S, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Doerfler A (2011) Flat-detector computed tomography in the assessment of intracranial stents: comparison with multi detector CT and conventional angiography in a new animal model. Eur Radiol 21:1779–1787
Struffert T, Kloska S, Engelhorn T, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Ott S, Doelken M, Saake M, Köhrmann M, Doerfler A (2011) Optimized intravenous Flat Detector CT for non-invasive visualization of intracranial stents: first results. Eur Radiol 21:411–418
Psychogios MN, Schramm P, Buhk JH, Xyda A, Gröschel K, Jung K, Knauth M (2010) Angiographic CT after intravenous contrast agent application: a noninvasive follow-up tool after intracranial angioplasty and stenting. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1886–1891
Struffert T, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Kloska S, Engelhorn T, Strother CM, Kalender WA, Köhrmann M, Schwab S, Doerfler A (2010) Flat detector CT in the evaluation of brain parenchyma, intracranial vasculature, and cerebral blood volume: a pilot study in patients with acute symptoms of cerebral ischemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1462–1469
Benndorf G, Claus B, Strother CM, Chang L, Klucznik RP (2006) Increased cell opening and prolapse of struts of a neuroform stent in curved vasculature: value of angiographic computed tomography: technical case report. Neurosurgery 58:ONS-E380
Hinkmann FM, Voit HL, Anders K, Baum U, Seidensticker P, Bautz WA, Lell MM (2009) Ultra-fast carotid CT-angiography: low versus standard volume contrast material protocol for a 128-slice CT-system. Invest Radiol 44:257–264
Kamran M, Yarnold J, Grunwald IQ, Byrne JV (2010) Assessment of angiographic outcomes after flow diversion treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a new grading schema. Neuroradiology 53:501–508
Walcott BP, Pisapia JM, Nahed BV, Kahle KT, Ogilvy CS (2011) Early experience with flow diverting endoluminal stents for the treatment of intracranial aneurysms. J Clin Neurosci 18:891–894
Strobel N, Meissner O, Boese J, Brunner T, Heigl B, Hoheisel M, Lauritsch G, Nagel M, Pfister M, Rührnschopf EP, Scholz B, Schreiber B, Spahn M, Zellerhoff M, Klingenbeck-Regn K (2009) 3D Imaging with Flat-Detector C-Arm systems. In: Reiser MF, Becker CR, Nikolaou K, Glazer G (eds) Multislice CT, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 33–51
Ulzheimer S, Flohr T (2009) Multislice CT: current technology and future developments. In: Reiser MF, Becker CR, Nikolaou K, Glazer G (eds) Multislice CT, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 3–23
Trossbach M, Hartmann M, Braun C, Sartor K, Hähnel S (2004) Small vessel stents for intracranial angioplasty: in vitro evaluation of in-stent stenoses using CT angiography. Neuroradiology 46:459–463
Ionescu M, Metcalfe RW, Cody D, Alvarado MV, Hipp J, Benndorf G (2011) Spatial resolution limits of multislice computed tomography (MS-CT), C-arm-CT, and flat panel-CT (FP-CT) compared to microCT for visualization of a small metallic stent. Acad Radiol 18:866–875
Cohnen M, Wittsack HJ, Assadi S, Muskalla K, Ringelstein A, Poll LW, Saleh A, Mödder U (2006) Radiation exposure of patients in comprehensive computed tomography of the head in acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1741–1745
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author contributions
The following the authors’ contributions to the study: guarantor of integrity of the entire study (MS and AD); study concepts (MS, TS and AD); study design (MS, TS and AD); definition of intellectual content (MS, TS and AD); literature research (MS, FS and SO); clinical studies (n.a.); experimental studies (n.a.); data acquisition (MS, TS, SO and PG); data analysis (MS and PG); statistical analysis (MS); manuscript preparation (MS, TS and AD); manuscript editing (MS); and manuscript review (TS, FS, OG and AD).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saake, M., Struffert, T., Goelitz, P. et al. Angiographic CT with intravenous contrast agent application for monitoring of intracranial flow diverting stents. Neuroradiology 54, 727–735 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0965-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0965-9