Abstract
Objective
To demonstrate the feasibility of intravenous Flat Detector CT Angiography (FD-CTA) for visualisation of intracranial Flow Diverting Devices. Flow Diverting Devices are used increasingly for treatment of intracranial aneurysms. A close follow up is necessary because it becomes obvious that a significant proportion of aneurysms treated with these devices remain patent. A minimally invasive method is highly desirable.
Methods
In two patients treated with flow diverters a Flat Detector CT (FD-CT) with intravenous contrast medium application was performed. Post-processing was performed using commercially available software.
Results
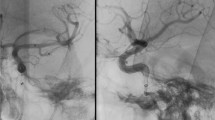
In both patients the lumen of the device and the lumen of the aneurysm could be clearly evaluated. Some beam hardening artefacts due to the marker wires of the device were obvious.
Conclusion
Flat Detector CT with intravenous contrast material application to evaluate flow-diverting devices seems to be feasible. Further studies are necessary to perform comparative evaluation of FD-CTA with angiography and other techniques like MRA or conventional CT angiography.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fiorella D, Hsu D, Woo HH, Tarr RW, Nelson PK (2010) Very late thrombosis of a pipeline embolization device construct: case report. Neurosurgery Suppl 67:E313–E314
Lubicz B, Collignon L, Raphaeli G, Pruvo JP, Bruneau M, De Witte O et al (2010) Flow-diverter stent for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a prospective study in 29 patients with 34 aneurysms. Stroke 41:2247–2253
Kulcsár Z, Houdart E, Bonafé A, Parker G, Millar J, Goddard AJ et al (2011) Intra-aneurysmal thrombosis as a possible cause of delayed aneurysm rupture after flow-diversion treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:20–25
Turowski B, Macht S, Kulcsár Z, Hänggi D, Stummer W (2011) Early fatal hemorrhage after endovascular cerebral aneurysm treatment with a flow diverter (SILK-Stent): do we need to rethink our concepts? Neuroradiology 53:37–41
Willinsky RA, Taylor SM, TerBrugge K, Farb RI, Tomlinson G, Montanera W et al (2003) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: prospective analysis of 2,899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 227:522–528
Struffert T, Kloska S, Engelhorn T, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Ott S, Doelken M et al (2010) Optimized intravenous flat detector CT for non-invasive visualization of intracranial stents: first results. Eur Radiol 21:411–418
Struffert T, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Kloska S, Engelhorn T, Strother CM, Kalender WA et al (2010) Flat detector CT in the evaluation of brain parenchyma, intracranial vasculature, and cerebral blood volume: a pilot study in patients with acute symptoms of cerebral ischemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1462–1469
Kyriakou Y, Richter G, Dörfler A, Kalender WA (2008) Neuroradiologic applications with routine C-arm flat panel detector CT: evaluation of patient dose measurements. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1930–1936
Szikora I, Berentei Z, Kulcsar Z, Marosfoi M, Vajda ZS, Lee W et al (2010) Treatment of intracranial aneurysms by functional reconstruction of the parent artery: the Budapest experience with the pipeline embolization device. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1139–1147
Kamran M, Yarnold J, Grunwald IQ, Byrne JV (2010) Assessment of angiographic outcomes after flow diversion treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a new grading schema. Neuroradiology. doi:10.1007/s00234-010-0767-5
O’Kelly CJ, Krings T, Fiorella D, Marotta TR (2010) A novel grading scale for the angiographic assessment of intracranial aneurysms treated using flow diverting stents. Interv Neuroradiol 16:133–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Struffert, T., Saake, M., Ott, S. et al. Intravenous flat detector CT angiography for non-invasive visualisation of intracranial flow diverter: technical feasibility. Eur Radiol 21, 1797–1801 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2113-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2113-7