Abstract
Introduction
Since the flow diverters (FDs) have been introduced it is possible to treat aneurysms that are considered difficult or impossible to treat with usual endovascular or surgical methods. It is still uncertain which aneurysms are suitable for this new treatment. We present the periprocedural complications, immediate result, late complications, imaging follow-up at 6 and 12 months and clinical follow-up at 2–23 months.
Methods
Twenty-two patients with 26 wide-necked or blister-like aneurysms had 23 treatments with implantation of a Silk stent. Eleven patients had re-canalizations, and 11 patients were either untreated or had been treated for another aneurysm.
Results
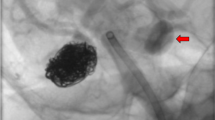
Periprocedural complications were seen in four treatments (17%). However, none of these had clinical consequences. Mortality and morbidity rates were 1 of 22 (5%) and 1 of 22 (5%), respectively. Clinical outcome was unchanged in 16 patients (72%), 3 patients improved (14%) and 3 patients worsened (14%). The end-of-procedure angiography did not show complete occlusion of any of the aneurysms, but at 6 months follow-up angiography, 17 of 25 aneurysms (68%) were completely occluded, and at 12 months, 18 of 21 aneurysms (86%) were occluded.
Conclusion
The effect of the Silk FD in terms of occlusion of the aneurysms seems to occur mainly during the first 6 months after placement but continues during the following time. Most delayed complications occur immediately after discontinuing the anticoagulation medication. Considering the complexity of the aneurysms treated, the rate of complications is acceptable.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, Sandercock P, Clarke M, Shrimpton J, Holman R (2002) International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet 360:1267–1274
Piotin M, Blanc R, Spelle L, Mounayer C, Piantino R, Schmidt PJ, Moret J (2010) Stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms: clinical and angiographic results in 216 consecutive aneurysms. Stroke 41:110–115
Fiorella D, Lylyk P, Szikora I, Kelly ME, Albuquerque FC, McDougall CG, Nelson PK (2009) Curative cerebrovascular reconstruction with the Pipeline embolization device: the emergence of definitive endovascular therapy for intracranial aneurysms. J NeuroIntervent Surg 1:56–65
Byrne JV, Beltechi R, Yarnold JA, Birks J, Kamran M (2010) Early experience in the treatment of intra-cranial aneurysms by endovascular flow diversion: a multicentre prospective study. PLoS One 5(9)
Cirillo L, Dall'olio M, Princiotta C, Simonetti A, Stafa A, Toni F, Leonardi M (2010) The use of flow-diverting stents in the treatment of giant cerebral aneurysms: preliminary results. J Neuroradiol 23:220–224
Kulcsár Z, Ernemann U, Wetzel SG, Bock A, Goericke S, Panagiotopoulos V, Forsting M, Ruefenacht DA, Wanke I (2010) High-profile flow diverter (Silk) implantation in the basilar artery: efficacy in the treatment of aneurysms and the role of the perforators. Stroke 41:1690–1696
Lubicz B, Collignon L, Raphaeli G, Pruvo JP, Bruneau M, De WO, Leclerc X (2010) Flow-diverter stent for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a prospective study in 29 patients with 34 aneurysms. Stroke 41:2247–2253
Lylyk P, Miranda C, Ceratto R, Ferrario A, Scrivano E, Luna HR, Berez AL, Tran Q, Nelson PK, Fiorella D (2009) Curative endovascular reconstruction of cerebral aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device: the Buenos Aires experience. Neurosurgery 64:632–642
Nelson PK, Lylyk P, Szikora I, Wetzel SG, Wanke I, Fiorella D (2011) The pipeline embolization device for the intracranial treatment of aneurysms trial. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:34–40
Szikora I, Berentei Z, Kulcsár Z, Marosfoi M, Vajda ZS, Lee W, Berez A, Nelson PK (2010) Treatment of intracranial aneurysms by functional reconstruction of the parent artery: the Budapest experience with the pipeline embolization device. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1139–1147
Fiorella D, Woo HH, Albuquerque FC, Nelson PK (2008) Definitive reconstruction of circumferential, fusiform intracranial aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device. Neurosurgery 62:1115–1120
Fiorella D, Kelly ME, Albuquerque FC, Nelson PK (2009) Curative reconstruction of a giant midbasilar trunk aneurysm with the pipeline embolization device. Neurosurgery 64:212–217
Kulcsár Z, Wetzel SG, Augsburger L, Gruber A, Wanke I, Rufenacht DA (2010) Effect of flow diversion treatment on very small ruptured aneurysms. Neurosurgery 67:789–793
Pumar JM, Garcia-Dorrego R, Nieto A, Vazquez-Herrero F, Blanco-Ulla M, Vazquez-Martin A (2010) Vascular reconstruction of a fusiform basilar aneurysm with the Silk embolization device. J NeuroIntervent Surg. doi:10.1136/jnis.2010.002725
Turowski B, Macht S, Kulcsár Z, Hanggi D, Stummer W (2011) Early fatal hemorrhage after endovascular cerebral aneurysm treatment with a flow diverter (SILK-Stent): do we need to rethink our concepts? Neuroradiology 53:37–41
Kulcsár Z, Houdart E, Bonafe A, Parker G, Millar J, Goddard AJ, Renowden S, Gal G, Turowski B, Mitchell K, Gray F, Rodriguez M, van den Berg R, Gruber A, Desal H, Wanke I, Rufenacht DA (2011) Intra-aneurysmal thrombosis as a possible cause of delayed aneurysm rupture after flow-diversion treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:20–25
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner, A., Cortsen, M., Hauerberg, J. et al. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Reconstruction of the parent artery with flow-diverting (Silk) stent. Neuroradiology 54, 709–718 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0949-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0949-9