Abstract
Introduction
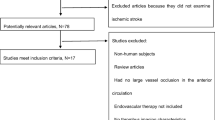
More insights in the etiopathogenesis of thrombi could be helpful in the treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke. The aim of our study was to determine the relationship between presence of a hyperdense vessel sign and thrombus density with different stroke subtypes.
Methods
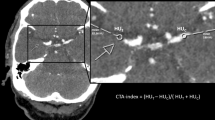
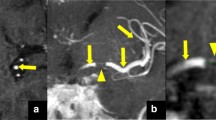
We included 123 patients with acute ischemic anterior circulation stroke and a visible occlusion on CT-angiography caused by cardioembolism (n = 53), large artery atherosclerosis (n = 55), or dissection (n = 15). Presence or absence of a hyperdense vessel sign was assessed and thrombus density was measured in Hounsfield Units (HU) on non-contrast 1 mm thin slices CT. Subsequently, occurrence of hyperdense vessel sign and thrombus density (absolute HU and rHU (=HU thrombus/HU contralateral)) were related with stroke subtypes.
Results
The presence of hyperdense vessel signs differed significantly among subtypes and was found in 45, 64 and 93 % of patients with cardioembolism, large artery atherosclerosis and dissection, respectively (p = 0.003). The mean HU and rHU (+95 % CI) of the thrombi in all vessels were respectively 56.1 (53.2–59.0) and 1.39 (1.33–1.45) in cardioembolism, 64.6 (62.2–66.9) and 1.59 (1.54–1.64) in large artery atherosclerosis and 76.4 (73.0–79.8) and 1.88 (1.79–1.97) in dissection (p < 0.0001). We found the same significant ranking order in the density of thrombi with hyperdense vessel signs (mean HU and rHU (+95 % CI), respectively): cardioembolism 61.3 (57.4–65.3) and 1.49 (57.4–65.3); large artery atherosclerosis 67.3 (64.9–69.7) and 1.65 (1.58–1.71); dissection 76.4 (72.6–80.1) and 1.89 (1.79–1.99, p < 0.0001).
Conclusion
Presence of a hyperdense vessel sign and thrombus density are related to stroke subtype.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carod-Artal FJ, Egido JA (2009) Quality of life after stroke: the importance of a good recovery. Cerebrovasc Dis 27(Suppl 1):204–214
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Makuc DM, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, Moy CS, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino ME, Nichol G, Paynter NP, Soliman EZ, Sorlie PD, Sotoodehnia N, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB (2012) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2012 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 125:e2–e220
Williams GR, Jiang JG, Matchar DB, Samsa GP (1999) Incidence and occurrence of total (first-ever and recurrent) stroke. Stroke 30:2523–2528
Bejot Y, Caillier M, Ben Salem D, Couvreur G, Rouaud O, Osseby GV, Durier J, Marie C, Moreau T, Giroud M (2008) Ischaemic stroke subtypes and associated risk factors: a French population based study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:1344–1348
Schulz UG, Rothwell PM (2003) Differences in vascular risk factors between etiological subtypes of ischemic stroke: importance of population-based studies. Stroke 34:2050–2059
Kolominsky-Rabas PL, Weber M, Gefeller O, Neundoerfer B, Heuschmann PU (2001) Epidemiology of ischemic stroke subtypes according to TOAST criteria: incidence, recurrence, and long-term survival in ischemic stroke subtypes: a population-based study. Stroke 32:2735–2740
Putaala J, Metso AJ, Metso TM, Konkola N, Kraemer Y, Haapaniemi E, Kaste M, Tatlisumak T (2009) Analysis of 1008 consecutive patients aged 15 to 49 with first-ever ischemic stroke: the Helsinki young stroke registry. Stroke 40:1195–1203
Mazighi M, Serfaty JM, Labreuche J, Laissy JP, Meseguer E, Lavallee PC, Cabrejo L, Slaoui T, Guidoux C, Lapergue B, Klein IF, Olivot JM, Abboud H, Simon O, Niclot P, Nifle C, Touboul PJ, Raphaeli G, Gohin C, Claeys ES, Amarenco P (2009) Comparison of intravenous alteplase with a combined intravenous-endovascular approach in patients with stroke and confirmed arterial occlusion (RECANALISE study): a prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol 8:802–809
Caplan LR (2006) Antiplatelet therapy in stroke prevention: present and future. Cerebrovasc Dis 21(Suppl 1):1–6
Jang IK, Gold HK, Ziskind AA, Fallon JT, Holt RE, Leinbach RC, May JW, Collen D (1989) Differential sensitivity of erythrocyte-rich and platelet-rich arterial thrombi to lysis with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator. A possible explanation for resistance to coronary thrombolysis. Circulation 79:920–928
Zivin JA, Fisher M, DeGirolami U, Hemenway CC, Stashak JA (1985) Tissue plasminogen activator reduces neurological damage after cerebral embolism. Science 230:1289–1292
Niessen F, Hilger T, Hoehn M, Hossmann KA (2003) Differences in clot preparation determine outcome of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator treatment in experimental thromboembolic stroke. Stroke 34:2019–2024
Molina CA, Montaner J, Arenillas JF, Ribo M, Rubiera M, Alvarez-Sabin J (2004) Differential pattern of tissue plasminogen activator-induced proximal middle cerebral artery recanalization among stroke subtypes. Stroke 35:486–490
Cho KH, Lee DH, Kwon SU, Choi CG, Kim SJ, Suh DC, Kim JS, Kang DW (2012) Factors and outcomes associated with recanalization timing after thrombolysis. Cerebrovasc Dis 33:255–261
Puig J, Pedraza S, Demchuk A, Daunis IEJ, Termes H, Blasco G, Soria G, Boada I, Remollo S, Banos J, Serena J, Castellanos M (2012) Quantification of thrombus hounsfield units on noncontrast CT predicts stroke subtype and early recanalization after intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:90–96
Wohner N (2008) Role of cellular elements in thrombus formation and dissolution. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med chem 6:224–228
Kirchhof K, Welzel T, Mecke C, Zoubaa S, Sartor K (2003) Differentiation of white, mixed, and red thrombi: value of CT in estimation of the prognosis of thrombolysis phantom study. Radiology 228:126–130
Kim EY, Heo JH, Lee SK, Kim DJ, Suh SH, Kim J, Kim DI (2006) Prediction of thrombolytic efficacy in acute ischemic stroke using thin-section noncontrast CT. Neurology 67:1846–1848
New PF, Aronow S (1976) Attenuation measurements of whole blood and blood fractions in computed tomography. Radiology 121:635–640
Liebeskind DS, Sanossian N, Yong WH, Starkman S, Tsang MP, Moya AL, Zheng DD, Abolian AM, Kim D, Ali LK, Shah SH, Towfighi A, Ovbiagele B, Kidwell CS, Tateshima S, Jahan R, Duckwiler GR, Vinuela F, Salamon N, Villablanca JP, Vinters HV, Marder VJ, Saver JL (2011) CT and MRI early vessel signs reflect clot composition in acute stroke. Stroke 42:1237–1243
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE 3rd (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 24:35–41
Kim YK, Schulman S (2009) Cervical artery dissection: pathology, epidemiology and management. Thromb Res 123:810–821
Chen CJ, Tseng YC, Lee TH, Hsu HL, See LC (2004) Multisection CT angiography compared with catheter angiography in diagnosing vertebral artery dissection. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:769–774
Leys D, Pruvo JP, Godefroy O, Rondepierre P, Leclerc X (1992) Prevalence and significance of hyperdense middle cerebral artery in acute stroke. Stroke 23:317–324
Rauch RA, Bazan C 3rd, Larsson EM, Jinkins JR (1993) Hyperdense middle cerebral arteries identified on CT as a false sign of vascular occlusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:669–673
Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Hudon ME, Pexman JH, Hill MD, Buchan AM (2001) Hyperdense sylvian fissure MCA "dot" sign: a CT marker of acute ischemia. Stroke 32:84–88
Bastianello S, Pierallini A, Colonnese C, Brughitta G, Angeloni U, Antonelli M, Fantozzi LM, Fieschi C, Bozzao L (1991) Hyperdense middle cerebral artery CT sign. Comparison with angiography in the acute phase of ischemic supratentorial infarction. Neuroradiology 33:207–211
Moulin T, Tatu L, Vuillier F, Cattin F (1999) Brain CT scan for acute cerebral infarction: early signs of ischemia. Rev Neurol 155:649–655
Chaves CJ, Caplan LR (2000) Heparin and oral anticoagulants in the treatment of brain ischemia. J Neurol Sci 173:3–9
Vila A, Korytowski W, Girotti AW (2002) Spontaneous transfer of phospholipid and cholesterol hydroperoxides between cell membranes and low-density lipoprotein: assessment of reaction kinetics and prooxidant effects. Biochemistry 41:13705–13716
Kockx MM, Cromheeke KM, Knaapen MW, Bosmans JM, De Meyer GR, Herman AG, Bult H (2003) Phagocytosis and macrophage activation associated with hemorrhagic microvessels in human atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:440–446
Kolodgie FD, Gold HK, Burke AP, Fowler DR, Kruth HS, Weber DK, Farb A, Guerrero LJ, Hayase M, Kutys R, Narula J, Finn AV, Virmani R (2003) Intraplaque hemorrhage and progression of coronary atheroma. N Engl J Med 349:2316–2325
Takaya N, Yuan C, Chu B, Saam T, Polissar NL, Jarvik GP, Isaac C, McDonough J, Natiello C, Small R, Ferguson MS, Hatsukami TS (2005) Presence of intraplaque hemorrhage stimulates progression of carotid atherosclerotic plaques: a high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging study. Circulation 111:2768–2775
Rao DS, Goldin JG, Fishbein MC (2005) Determinants of plaque instability in atherosclerotic vascular disease. Cardiovasc Pathol Off J Soc Cardiovasc Pathol 14:285–293
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV, Gold HK, Tulenko TN, Wrenn SP, Narula J (2005) Atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability to rupture: angiogenesis as a source of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:2054–2061
Redgrave JN, Lovett JK, Gallagher PJ, Rothwell PM (2006) Histological assessment of 526 symptomatic carotid plaques in relation to the nature and timing of ischemic symptoms: the Oxford plaque study. Circulation 113:2320–2328
Wysokinski WE, Owen WG, Fass DN, Patrzalek DD, Murphy L, McBane RD 2nd (2004) Atrial fibrillation and thrombosis: immunohistochemical differences between in situ and embolized thrombi. J thromb haemost JTH 2:1637–1644
Mohan IV (2013) Current optimal assessment and management of carotid and vertebral spontaneous and traumatic dissection. Angiology. doi:10.1177/0003319712475154
Stevic I, Chan HH, Chan AK (2011) Carotid artery dissections: thrombosis of the false lumen. Thromb Res 128:317–324
Marder VJ, Chute DJ, Starkman S, Abolian AM, Kidwell C, Liebeskind D, Ovbiagele B, Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Jahan R, Vespa PM, Selco S, Rajajee V, Kim D, Sanossian N, Saver JL (2006) Analysis of thrombi retrieved from cerebral arteries of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 37:2086–2093
Almekhlafi MA, Hu WY, Hill MD, Auer RN (2008) Calcification and endothelialization of thrombi in acute stroke. Ann Neurol 64:344–348
Bhatia R, Hill MD, Shobha N, Menon B, Bal S, Kochar P, Watson T, Goyal M, Demchuk AM (2010) Low rates of acute recanalization with intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in ischemic stroke: real-world experience and a call for action. Stroke 41:2254–2258
Khatri P, Abruzzo T, Yeatts SD, Nichols C, Broderick JP, Tomsick TA (2009) Good clinical outcome after ischemic stroke with successful revascularization is time-dependent. Neurology 73:1066–1072
Wu JH, Siddiqui K, Diamond SL (1994) Transport phenomena and clot dissolving therapy: an experimental investigation of diffusion-controlled and permeation-enhanced fibrinolysis. Thromb Haemost 72:105–112
Blinc A, Keber D, Lahajnar G, Stegnar M, Zidansek A, Demsar F (1992) Lysing patterns of retracted blood clots with diffusion or bulk flow transport of plasma with urokinase into clots—a magnetic resonance imaging study in vitro. Thromb Haemost 68:667–671
Moftakhar P, English JD, Cooke DL, Kim WT, Stout C, Smith WS, Dowd CF, Higashida RT, Halbach VV, Hetts SW (2013) Density of thrombus on admission ct predicts revascularization efficacy in large vessel occlusion acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 44:243–245
Rocha S, Pires A, Gomes J, Rocha J, Sousa F, Pinho J, Rodrigues M, Ferreira C, Machado A, Mare R, Fontes JR (2011) Intravenous thrombolysis is more effective in ischemic cardioembolic strokes than in non-cardioembolic? Arq Neuropsiquiatr 69:905–909
Hsia AW, Sachdev HS, Tomlinson J, Hamilton SA, Tong DC (2003) Efficacy of IV tissue plasminogen activator in acute stroke: does stroke subtype really matter? Neurology 61:71–75
Mustanoja S, Meretoja A, Putaala J, Viitanen V, Curtze S, Atula S, Artto V, Happola O, Kaste M (2011) Outcome by stroke etiology in patients receiving thrombolytic treatment: descriptive subtype analysis. Stroke 42:102–106
Grau AJ, Weimar C, Buggle F, Heinrich A, Goertler M, Neumaier S, Glahn J, Brandt T, Hacke W, Diener HC (2001) Risk factors, outcome, and treatment in subtypes of ischemic stroke: the German stroke data bank. Stroke 32:2559–2566
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
The following individuals and institutions constitute the DUST Study University Medical Center Utrecht, The Netherlands Department of Radiology B.K. Velthuis, T. van Seeters, I.C. van der Schaaf, J.M. Niesten, J.W. Dankbaar, W.P.T.M. Mali; Department of Neurology M.J.A. Luitse, G.J. Biessels, L.J. Kappelle; Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care Y. van der Graaf; Academic Medical Center Amsterdam, The Netherlands Department of Radiology C.B.L.M. Majoie, L.F.M. Beenen; Department of Neurology Y.B. Roos; Catharina Hospital Eindhoven, The Netherlands Department of Radiology L.E.M. Duijm; Department of Neurology K. Keizer; Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam, The Netherlands Department of Radiology A. van der Lugt; Department of Neurology D.W.J. Dippel; Gelre Hospital Apeldoorn, The Netherlands Department of Radiology K.E. Droogh-de Greeve; Department of Neurology H.P. Bienfait; Leiden University Medical Center, The Netherlands Department of Radiology M.A.A. van Walderveen Department of Neurology M.J.H. Wermer; Medical Center Leeuwarden, The Netherlands Department of Radiology J. Dol; Department of Neurology W.J. Schuiling; Medical Center Haaglanden Den Haag, The Netherlands Department of Radiology G.J. Lycklama à Nijeholt; Department of Neurology J. Boiten; Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis Amsterdam, The Netherlands Department of Radiology D. Duyndam; Department of Neurology V.I.H. Kwa; Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Center, The Netherlands Department of Radiology A. Meijer; Department of Neurology E.J. van Dijk; Rijnstate Hospital Arnhem, The Netherlands Department of Radiology F.O.H.W. Kesselring, A.D. Horsch; Department of Neurology J. Hofmeijer; St. Antonius Hospital Nieuwegein, The Netherlands Department of Radiology J.A. Vos; Department of Neurology W.J. Schonewille; St. Elisabeth Hospital Tilburg, The Netherlands Department of Radiology W.J. van Rooij; Department of Neurology P.L.M. de Kort; St. Franciscus Hospital Rotterdam, The Netherlands; Department of Radiology C.C. Pleiter; Department of Neurology S.L.M. Bakker; VU Medical Center Amsterdam, The Netherlands Department of Radiology J. Bot; Department of Neurology M.C. Visser
Clinical Trial Registration Information URL: http://www.ClinicalTrials.gov.Unique-identifierNCT00880113
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niesten, J.M., van der Schaaf, I.C., Biessels, G.J. et al. Relationship between thrombus attenuation and different stroke subtypes. Neuroradiology 55, 1071–1079 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1217-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1217-y