Abstract
Purpose
Various software applications offer support in the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke (AIS), yet it remains unclear whether the performance of these tools is comparable to each other. Our study aimed to evaluate three fully automated software applications for Alberta Stroke Program Early CT (ASPECT) scoring (Syngo.via Frontier ASPECT Score Prototype V2, Brainomix e-ASPECTS® and RAPID ASPECTS) in AIS patients.
Methods
Retrospectively, 131 patients with large vessel occlusion (LVO) of the middle cerebral artery or the internal carotid artery, who underwent endovascular therapy (EVT), were included. Pre-interventional non-enhanced CT (NECT) datasets were assessed in random order using the automated ASPECT software and by three experienced neuroradiologists in consensus. Interclass correlation coefficient (ICC), Bland-Altman, and receiver operating characteristics (ROC) were applied for statistical analysis.
Results
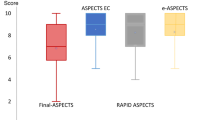
Median ASPECTS of the expert consensus reading was 8 (7–10). Highest correlation was between the expert read and Brainomix (r = 0.871 (0.818, 0.909), p < 0.001). Correlation between expert read and Frontier V2 (r = 0.801 (0.719, 0.859), p < 0.001) and between expert read and RAPID (r = 0.777 (0.568, 0.871), p < 0.001) was high, respectively. There was a high correlation among the software tools (Frontier V2 and Brainomix: r = 0.830 (0.760, 0.880), p < 0.001; Frontier V2 and RAPID: r = 0.847 (0.693, 0.913), p < 0.001; Brainomix and RAPID: r = 0.835 (0.512, 0.923), p < 0.001). An ROC curve analysis revealed comparable accuracy between the applications and expert consensus reading (Brainomix: AUC = 0.759 (0.670–0.848), p < 0.001; Frontier V2: AUC = 0.752 (0.660–0.843), p < 0.001; RAPID: AUC = 0.734 (0.634–0.831), p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Overall, there is a convincing yet developable grade of agreement between current ASPECT software evaluation tools and expert evaluation with regard to ASPECT assessment in AIS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hill MD, Demchuk AM, Goyal M, Jovin TG, Foster LD, Tomsick TA, von Kummer R, Yeatts SD, Palesch YY, Broderick JP (2014) Alberta Stroke Program early computed tomography score to select patients for endovascular treatment: Interventional Management of Stroke (IMS)-III trial. Stroke 45:444–449
Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Zhang J, Buchan AM (2000) Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. ASPECTS study group. Alberta Stroke Programme Early CT Score. Lancet 355:1670–1674
Pexman JH, Barber PA, Hill MD, Sevick RJ, Demchuk AM, Hudon ME, Hu WY, Buchan AM (2001) Use of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) for assessing CT scans in patients with acute stroke. Am J Neuroradiol 22:1534–1542
Yoo AJ, Berkhemer OA, PSS F, van den Berg LA, Beumer D, Lingsma HF, Schonewille WJ, Sprengers MES, van den Berg R, van Walderveen MAA, Beenen LFM, Wermer MJH, Nijeholt G, Boiten J, Jenniskens SFM, Bot JCJ, Boers AMM, Marquering HA, Roos Y, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Dippel DWJ, van der Lugt A, van Zwam WH, Majoie C (2016) Effect of baseline Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score on safety and efficacy of intra-arterial treatment: a subgroup analysis of a randomised phase 3 trial (MR CLEAN). Lancet Neurol 15:685–694
Yoo AJ, Zaidat OO, Chaudhry ZA, Berkhemer OA, Gonzalez RG, Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Mualem E, Ueda D, Buell H, Sit SP, Bose A (2014) Impact of pretreatment noncontrast CT Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score on clinical outcome after intra-arterial stroke therapy. Stroke 45:746–751
Bal S, Bhatia R, Menon BK, Shobha N, Puetz V, Dzialowski I, Modi J, Goyal M, Hill MD, Smith EE, Demchuk AM (2015) Time dependence of reliability of noncontrast computed tomography in comparison to computed tomography angiography source image in acute ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke 10:55–60
Farzin B, Fahed R, Guilbert F, Poppe AY, Daneault N, Durocher AP, Lanthier S, Boudjani H, Khoury NN, Roy D, Weill A, Gentric JC, Batista AL, Letourneau-Guillon L, Bergeron F, Henry MA, Darsaut TE, Raymond J (2016) Early CT changes in patients admitted for thrombectomy: intrarater and interrater agreement. Neurology 87:249–256
Forsting M (2017) Machine learning will change medicine. J Nucl Med 58:357–358
Obermeyer Z, Emanuel EJ (2016) Predicting the future-big data, machine learning, and clinical medicine. N Engl J Med 375:1216–1219
Erickson BJ, Korfiatis P, Akkus Z, Kline TL (2017) Machine learning for medical imaging. Radiographics 37:505–515
Lee EJ, Kim YH, Kim N, Kang DW (2017) Deep into the brain: artificial intelligence in stroke imaging. J Stroke 19:277–285
Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig L, Lijmer JG, Moher D, Rennie D, de Vet HC, Kressel HY, Rifai N, Golub RM, Altman DG, Hooft L, Korevaar DA, Cohen JF (2015) STARD 2015: an updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. BMJ 351:h5527
Koo TK, Li MY (2016) A guideline of selecting and reporting Intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med 15:155–163
Cicchetti DV, Sparrow SA (1981) Developing criteria for establishing interrater reliability of specific items: applications to assessment of adaptive behavior. Am J Ment Defic 86:127–137
Herweh C, Ringleb PA, Rauch G, Gerry S, Behrens L, Mohlenbruch M, Gottorf R, Richter D, Schieber S, Nagel S (2016) Performance of e-ASPECTS software in comparison to that of stroke physicians on assessing CT scans of acute ischemic stroke patients. Int J Stroke 11:438–445
Nagel S, Sinha D, Day D, Reith W, Chapot R, Papanagiotou P, Warburton EA, Guyler P, Tysoe S, Fassbender K, Walter S, Essig M, Heidenrich J, Konstas AA, Harrison M, Papadakis M, Greveson E, Joly O, Gerry S, Maguire H, Roffe C, Hampton-Till J, Buchan AM, Grunwald IQ (2017) e-ASPECTS software is non-inferior to neuroradiologists in applying the ASPECT score to computed tomography scans of acute ischemic stroke patients. Int J Stroke 12:615–622
Pfaff J, Herweh C, Schieber S, Schonenberger S, Bosel J, Ringleb PA, Mohlenbruch M, Bendszus M, Nagel S (2017) e-ASPECTS correlates with and is predictive of outcome after mechanical thrombectomy. Am J Neuroradiol 38:1594–1599
Goebel J, Stenzel E, Guberina N, Wanke I, Koehrmann M, Kleinschnitz C, Umutlu L, Forsting M, Moenninghoff C, Radbruch A (2018) Automated ASPECT rating: comparison between the Frontier ASPECT Score software and the Brainomix software. Neuroradiology 60:1267–1272
Goebel J, Stenzel E, Zuelow S, Kleinschnitz C, Forsting M, Moenninghoff C, Radbruch A (2019) Computer aided diagnosis for ASPECT rating: initial experiences with the Frontier ASPECT Score software. Acta Radiol 284185119842465
Murray NM, Unberath M, Hager GD, Hui FK (2019) Artificial intelligence to diagnose ischemic stroke and identify large vessel occlusions: a systematic review. J Neurointerv Surg
McKinley R, Hani L, Gralla J, El-Koussy M, Bauer S, Arnold M, Fischer U, Jung S, Mattmann K, Reyes M, Wiest R (2017) Fully automated stroke tissue estimation using random forest classifiers (FASTER). J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 37:2728–2741
Austein F, Wodarg F, Jurgensen N, Huhndorf M, Meyne J, Lindner T, Jansen O, Larsen N, Riedel C (2019) Automated versus manual imaging assessment of early ischemic changes in acute stroke: comparison of two software packages and expert consensus. Eur Radiol 29:6285–6292
Campbell BC, Christensen S, Levi CR, Desmond PM, Donnan GA, Davis SM, Parsons MW (2011) Cerebral blood flow is the optimal CT perfusion parameter for assessing infarct core. Stroke 42:3435–3440
Cereda CW, Christensen S, Campbell BCV, Mishra NK, Mlynash M, Levi C, Straka M, Wintermark M, Bammer R, Albers GW, Parsons MW, Lansberg MG (2016) A benchmarking tool to evaluate computer tomography perfusion infarct core predictions against a DWI standard. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:1780–1789
Lee TY, Murphy BD, Aviv RI, Fox AJ, Black SE, Sahlas DJ, Symons S, Lee DH, Pelz D, Gulka IB, Chan R, Beletsky V, Hachinski V, Hogan MJ, Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Coutts SB (2006) Cerebral blood flow threshold of ischemic penumbra and infarct core in acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review. Stroke 37:2201 author reply 2203
Wintermark M, Flanders AE, Velthuis B, Meuli R, van Leeuwen M, Goldsher D, Pineda C, Serena J, van der Schaaf I, Waaijer A, Anderson J, Nesbit G, Gabriely I, Medina V, Quiles A, Pohlman S, Quist M, Schnyder P, Bogousslavsky J, Dillon WP, Pedraza S (2006) Perfusion-CT assessment of infarct core and penumbra: receiver operating characteristic curve analysis in 130 patients suspected of acute hemispheric stroke. Stroke 37:979–985
Sheth SA, Malhotra K, Liebeskind DS, Liang CW, Yoo AJ, Jahan R, Nogueira RG, Pereira V, Gralla J, Albers G, Goyal M, Saver JL (2018) Regional contributions to poststroke disability in endovascular therapy. Interv Neurol 7:533–543
Gupta AC, Schaefer PW, Chaudhry ZA, Leslie-Mazwi TM, Chandra RV, Gonzalez RG, Hirsch JA, Yoo AJ (2012) Interobserver reliability of baseline noncontrast CT Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score for intra-arterial stroke treatment selection. Am J Neuroradiol 33:1046–1049
Kaesmacher J, Chaloulos-Iakovidis P, Panos L, Mordasini P, Michel P, Hajdu SD, Ribo M, Requena M, Maegerlein C, Friedrich B, Costalat V, Benali A, Pierot L, Gawlitza M, Schaafsma J, Mendes Pereira V, Gralla J, Fischer U (2019) Mechanical thrombectomy in ischemic stroke patients with Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score 0-5. Stroke 50:880–888
Broocks G, Kniep H, Schramm P, Hanning U, Flottmann F, Faizy T, Schonfeld M, Meyer L, Schon G, Aulmann L, Machner B, Royl G, Fiehler J, Kemmling A (2019) Patients with low Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) but good collaterals benefit from endovascular recanalization. J Neurointerv Surg:neurintsurg-2019-015308
Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, Dippel DW, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, Davalos A, Majoie CB, van der Lugt A, de Miquel MA, Donnan GA, Roos YB, Bonafe A, Jahan R, Diener HC, van den Berg LA, Levy EI, Berkhemer OA, Pereira VM, Rempel J, Millan M, Davis SM, Roy D, Thornton J, Roman LS, Ribo M, Beumer D, Stouch B, Brown S, Campbell BC, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Saver JL, Hill MD, Jovin TG (2016) Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 387:1723–1731
Kuang H, Najm M, Chakraborty D, Maraj N, Sohn SI, Goyal M, Hill MD, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Qiu W (2019) Automated ASPECTS on noncontrast CT scans in patients with acute ischemic stroke using machine learning. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 40:33–38
Menon BK, Puetz V, Kochar P, Demchuk AM (2011) ASPECTS and other neuroimaging scores in the triage and prediction of outcome in acute stroke patients. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 21:407–423 xii
Maegerlein C, Fischer J, Monch S, Berndt M, Wunderlich S, Seifert CL, Lehm M, Boeckh-Behrens T, Zimmer C, Friedrich B (2019) Automated calculation of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score: feasibility and reliability. Radiology 291:141–148
Mokin M, Primiani CT, Siddiqui AH, Turk AS (2017) ASPECTS (Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score) measurement using Hounsfield unit values when selecting patients for stroke thrombectomy. Stroke 48:1574–1579
Labeyrie MA, Turc G, Hess A, Hervo P, Mas JL, Meder JF, Baron JC, Touze E, Oppenheim C (2012) Diffusion lesion reversal after thrombolysis: a MR correlate of early neurological improvement. Stroke 43:2986–2991
Altman DG (1980) Statistics and ethics in medical research. VII-interpreting results. Br Med J 281:1612–1614
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Disclaimer
The Department of Neuroradiology, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, has a research agreement with Siemens Healthcare GmbH (Forchheim, Germany), with Brainomix Ltd. (Oxford, United Kingdom) and with iSchemaView, Inc. (Menlo Park, CA, USA).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoelter, P., Muehlen, I., Goelitz, P. et al. Automated ASPECT scoring in acute ischemic stroke: comparison of three software tools. Neuroradiology 62, 1231–1238 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02439-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02439-3