Abstract
Objective
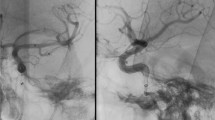
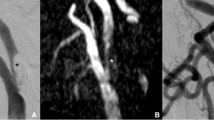
As stents for treating intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis may develop in-stent re-stenosis (ISR) in up to 30%, follow-up imaging is mandatory. Residual stenosis (RS) is not rare. We evaluated an optimised Flat Detector CT protocol with intravenous contrast material application (i.v. FD-CTA) for non-invasive follow-up.
Methods
In 12 patients with intracranial stents, follow-up imaging was performed using i.v. FD-CTA. MPR, subtracted MIP and VRT reconstructions were used to correlate to intra-arterial angiography (DSA). Two neuroradiologists evaluated the images in anonymous consensus reading and calculated the ISR or RS. Correlation coefficients and a Wilcoxon test were used for statistical analysis.
Results
In 4 patients, no stenosis was detected. In 6 patients RS and in two cases ISR by intima hyperplasia perfectly visible on MPR reconstructions of i.v. FD-CTA were detected. Wilcoxon’s test showed no significant differences between the methods (p > 0.05). We found a high correlation with coefficients of the pairs DSA/ FD-CT MIP r = 0.91, DSA/ FD-CT MPR r = 0.82 and FD-CT MIP/ FD-CT MPR r = 0.8.
Conclusion
Intravenous FD-CTA could clearly visualise the stent and the lumen, allowing ISR or RS to be recognised. FD-CTA provides a non-invasive depiction of intracranial stents and might replace DSA for non-invasive follow-up imaging.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bose A, Hartmann M, Henkes H, Liu HM, Teng MM, Szikora I et al (2007) A novel, self-expanding, nitinol stent in medically refractory intracranial atherosclerotic stenoses: the Wingspan study. Stroke 38:1531–1537
Levy EI, Turk AS, Albuquerque FC, Niemann DB, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Pride L et al (2007) Wingspan in-stent restenosis and thrombosis: incidence, clinical presentation, and management. Neurosurgery 61:644–650
Fiorella DJ, Levy EI, Turk AS, Albuquerque FC, Pride GL Jr, Woo HH et al (2009) Target lesion revascularization after wingspan: assessment of safety and durability. Stroke 40:106–110
Trossbach M, Hartmann M, Braun C, Sartor K, Hähnel S (2004) Small vessel stents for intracranial angioplasty: in vitro evaluation of in-stent stenoses using CT angiography. Neuroradiology 46:459–463
Willinsky RA, Taylor SM, TerBrugge K, Farb RI, Tomlinson G, Montanera W (2003) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: prospective analysis of 2, 899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 227:522–528
Kalender WA, Kyriakou Y (2007) Flat-detector computed tomography (FD-CT). Eur Radiol 17:2767–2779
Kalender WA (2003) The use of flat-panel detectors for CT imaging. Radiologe 43:379–387
Benndorf G, Strother CM, Claus B, Naeini R, Morsi H, Klucznik R et al (2005) Angiographic CT in cerebrovascular stenting. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1813–1818
Benndorf G, Klucznik RP, Strother CM (2006) Images in cardiovascular medicine: angiographic computed tomography for imaging of underdeployed intracranial stent. Circulation 114:e499–500
Struffert T, Doelken M, Adamek E, Schwarz M, Engelhorn T, Kloska S et al (2010) Flat-detector computed tomography with intravenous contrast material application in experimental aneurysms: comparison with multislice CT and conventional angiography. Acta Radiol 51:431–437
Struffert T, Deuerling-Zheng Y, Kloska S, Engelhorn T, Strother CM, Kalender WA et al (2010) A Flat Detector CT in the evaluation of brain parenchyma, intracranial vasculature, and cerebral blood volume: a pilot study in patients with acute symptoms of cerebral ischemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2083
Buhk JH, Lingor P, Knauth M (2008) Angiographic CT with intravenous administration of contrast medium is a noninvasive option for follow-up after intracranial stenting. Neuroradiology 50:349–354
Benndorf G, Claus B, Strother CM, Chang L, Klucznik RP (2006) Increased cell opening and prolapse of struts of a neuroform stent in curved vasculature: value of angiographic computed tomography: technical case report. Neurosurgery 4(Suppl 2):ONS-E380, discussion ONS-E380
Nguyen-Huynh MN, Wintermark M, English J (2008) How accurate is CT angiography in evaluating intracranial atherosclerotic disease? Stroke 39:1184–1188
SSYLVIA Study Investigators (2004) Stenting of Symptomatic Atherosclerotic Lesions in the Vertebral or Intracranial Arteries (SSYLVIA): study results. Stroke 35:1388–1392
Hartmann M, Jansen O (2005) Angioplasty and stenting of intracranial stenosis. Curr Opin Neurol 18:39–45
Prabhakaran S, Warrior L, Wells KR, Jhaveri MD, Chen M, Lopes DK (2009) The utility of quantitative magnetic resonance angiography in the assessment of intracranial in-stent stenosis. Stroke 40:991–993
Turk AS, Rowley HA, Niemann DB, Fiorella D, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Pulfer K et al (2007) CT angiographic appearance of in-stent restenosis of intracranial arteries treated with the Wingspan stent. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1752–1754
Buerke B, Wittkamp G, Seifarth H, Heindel W, Kloska SP (2009) Dual-energy CTA with bone removal for transcranial arteries: intraindividual comparison with standard CTA without bone removal and TOF-MRA. Acad Radiol 16:1348–1355
Albuquerque FC, Levy EI, Turk AS, Niemann DB, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Pride GL Jr (2008) Angiographic patterns of Wingspan in-stent restenosis. Neurosurgery 63:23–27
Prell D, Kyriakou Y, Struffert T, Dörfler A, Kalender WA (2010) Metal artifact reduction for clipping and coiling in interventional C-arm CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:634–649
Buhk JH, Kallenberg K, Mohr A, Dechent P, Knauth M (2009) Evaluation of angiographic computed tomography in the follow-up after endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms–a comparative study with DSA and TOF-MRA. Eur Radiol 19:430–6
Acknowledgements
Yu Deuerling-Zheng is an employee of Siemens AG and provided installation of this new DynaCT program. The DynaCT program has got a CE mark.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Struffert, T., Kloska, S., Engelhorn, T. et al. Optimized intravenous Flat Detector CT for non-invasive visualization of intracranial stents: first results. Eur Radiol 21, 411–418 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1931-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1931-3