Summary
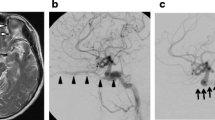
We treated 9 patients with the dural arteriovenous fistula involving the cavernous sinus by transvenous embolization. Two patients experienced deterioration of oculo-motor dysfunction after transvenous embolization. We can speculate about two different kind of causes by which patients symptoms deteriorated according to the result of intrasinus pressure recorded during the embolization [1]: high intrasinus pressure caused by the obliteration of the drainage pathway resulted in cranial nerve palsy in one case [2]; implanted coils directly compressed the cranial nerve in another case. Fortunately our cases recovered, but some kind of preventative measures may be needed in similar cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aihara, N., Mase, M., Yamada, K. et al. Deterioration of Ocular Motor Dysfunction After Transvenous Embolization of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Involving the Cavernous Sinus. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141, 707–710 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050365
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007010050365