Abstract
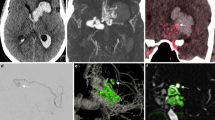
Time-resolved computed tomography angiography (4D-CTA) using a 320-row area detector CT scanner has recently been applied in the evaluation of cranial vascular disorders. However, application of 4D-CTA to spinal vascular disorder evaluation has never before been described. The authors herein report their initial experience of 4D-CTA in the evaluation of spinal arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) and compare this novel modality with other imaging modalities. Four consecutive patients with spinal AVF underwent time-resolved contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (trMRA), 4D-CTA, and selective catheter angiography (CA). In 4D-CTA, volume data was transformed into 3D volume-rendered images and maximum intensity projection. These images were also evaluated by time-resolved serial phases. Then, images of each modality were compared, focusing on the detection of perimedullary draining veins and the prediction of AVF location and drainage flow direction. All modalities successfully detected perimedullary draining veins in all cases. Location of the AVF was detected in all cases by CA. trMRA and 4D-CTA detected the AVF in three out of the four cases. With regard to flow direction, while 4D-CTA successfully depicted ascending or descending drainage flow in the spinal canal, CA failed to detect the flow direction in one case while trMRA failed in two cases. In the case with epidural AVF, 4D-CTA was the only technique to detect the flow direction of perimedullary drainage. Although this is only an initial experience of the application of 4D-CTA to spinal vascular diseases, 4D-CTA was capable of detecting the dynamic vascular flow of spinal AVFs. The authors believe that 4D-CTA can be a useful option in the evaluation of spinal AVFs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Cashen TA, Carroll TJ, McComb E, Muzaffar M, Shaibani A, Walker MT (2007) Time-resolved spinal MR angiography: initial clinical experience in the evaluation of spinal arteriovenous shunts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(9):1806–1810
Bertrand D, Douvrin F, Gerardin E, Clavier E, Proust F, Thiebot J (2004) Diagnosis of spinal dural arteriovenous fistula with multidetector row computed tomography: a case report. Neuroradiology 46(10):851–854
Bowen BC, Fraser K, Kochan JP, Pattany PM, Green BA, Quencer RM (1995) Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: evaluation with MR angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16(10):2029–2043
Brouwer PA, Bosman T, van Walderveen MA, Krings T, Leroux AA, Willems PW (2010) Dynamic 320-section CT angiography in cranial arteriovenous shunting lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31(4):767–770
Eddleman CS, Jeong H, Cashen TA, Walker M, Bendok BR, Batjer HH, Carroll TJ (2009) Advanced noninvasive imaging of spinal vascular malformations. Neurosurg Focus 26(1):E9
Farb RI, Kim JK, Willinsky RA, Montanera WJ, terBrugge K, Derbyshire JA, van Dijk JM, Wright GA (2002) Spinal dural arteriovenous fistula localization with a technique of first-pass gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography: initial experience. Radiology 222(3):843–850
Hayakawa M, Maeda S, Sadato A, Tanaka T, Kaito T, Hattori N, Ganaha T, Moriya S, Katada K, Murayama K, Kato Y, Hirose Y (2011) Detection of pulsation in ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysms by ECG-gated 3D-CT angiography (4D-CTA) with 320-row area detector CT (ADCT) and evaluation of its clinical usefulness. Neurosurgery 69(4):843–51
Hayakawa M, Murayama K, Katada K, Hirose Y (2011) Usefulness of 320-row area detector CT in neurosurgery. Jpn J Neurosurg 20(9):640–647
Jiang L, Huang CG, Liu P, Yan B, Chen JX, Chen HR, Bai RL, Lu YC (2008) 3-Dimensional rotational angiography for the treatment of spinal cord vascular malformations. Surg Neurol 69(4):369–373, discussion 373–364
Killory BD, Nakaji P, Maughan PH, Wait SD, Spetzler RF (2011) Evaluation of angiographically occult spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae with surgical microscope-integrated intraoperative near-infrared indocyanine green angiography: report of 3 cases. Neurosurgery 68(3):781–787, discussion 787
Klingebiel R, Siebert E, Diekmann S, Wiener E, Masuhr F, Wagner M, Bauknecht HC, Dewey M, Bohner G (2009) 4-D Imaging in cerebrovascular disorders by using 320-slice CT: feasibility and preliminary clinical experience. Acad Radiol 16(2):123–129
Lai PH, Pan HB, Yang CF, Yeh LR, Hsu SS, Lee KW, Weng MJ, Wu MT, Liang HL, Chen CK (2005) Multi-detector row computed tomography angiography in diagnosing spinal dural arteriovenous fistula: initial experience. Stroke 36(7):1562–1564, Epub 2005 Jun 1562
Luetmer PH, Lane JI, Gilbertson JR, Bernstein MA, Huston J 3rd, Atkinson JL (2005) Preangiographic evaluation of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas with elliptic centric contrast-enhanced MR Angiography and effect on radiation dose and volume of iodinated contrast material. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26(4):711–718
Luo Z, Wang D, Sun X, Zhang T, Liu F, Dong D, Chan NK, Shen B (2011) Comparison of the accuracy of subtraction CT angiography performed on 320-detector row volume CT with conventional CT angiography for diagnosis of intracranial aneurysms. Eur J Radiol 81(1):118–22
Morris JM, Kaufmann TJ, Campeau NG, Cloft HJ, Lanzino G (2011) Volumetric myelographic magnetic resonance imaging to localize difficult-to-find spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg Spine 14(3):398–404
Mull M, Nijenhuis RJ, Backes WH, Krings T, Wilmink JT, Thron A (2007) Value and limitations of contrast-enhanced MR angiography in spinal arteriovenous malformations and dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(7):1249–1258
Oldfield EH, Bennett A 3rd, Chen MY, Doppman JL (2002) Successful management of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas undetected by arteriography. Report of three cases. J Neurosurg 96(2 Suppl):220–229
Prestigiacomo CJ, Niimi Y, Setton A, Berenstein A (2003) Three-dimensional rotational spinal angiography in the evaluation and treatment of vascular malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24(7):1429–1435
Saladino A, Atkinson JL, Rabinstein AA, Piepgras DG, Marsh WR, Krauss WE, Kaufmann TJ, Lanzino G (2010) Surgical treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae: a consecutive series of 154 patients. Neurosurgery 67(5):1350–1357, discussion 1357–1358
Sharma AK, Westesson PL (2008) Preoperative evaluation of spinal vascular malformation by MR angiography: how reliable is the technique: case report and review of literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 110(5):521–524
Si-Jia G, Meng-Wei Z, Xi-Ping L, Yu-Shen Z, Jing-Hong L, Zhong-Hui W, Pei-Zhuo Z, Qiang S, Qiang W, Chuan-Sheng L, Ke X (2008) The clinical application studies of CT spinal angiography with 64-detector row spiral CT in diagnosing spinal vascular malformations. Eur J Radiol 20:20
Sugawara T, Hirano Y, Itoh Y, Kinouchi H, Takahashi S, Mizoi K (2007) Angiographically occult spinal dural arteriovenous fistula located using selective computed tomography angiography. Case report. J Neurosurg Spine 7(2):215–220
Valentin J (2007) Managing patient dose in multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT). ICRP Publication 102. Ann ICRP 37(1):1–79, iii
Vargas MI, Nguyen D, Viallon M, Kulcsar Z, Tessitore E, Rilliet B, Rufenacht D, Lovblad K (2010) Dynamic MR angiography (MRA) of spinal vascular diseases at 3 T. Eur Radiol 20(10):2491–2495
Willems PW, Brouwer PA, Barfett JJ, terBrugge KG, Krings T (2011) Detection and classification of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas using 4D-CT angiography: initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32(1):49–53
Willems PW, Taeshineetanakul P, Schenk B, Brouwer PA, Terbrugge KG, Krings T (2011) The use of 4D-CTA in the diagnostic work-up of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology 54(2):123–31
Yamaguchi S, Eguchi K, Kiura Y, Takeda M, Nagayama T, Uchida H, Ito Y, Hotta T, Arita K, Kurisu K (2007) Multi-detector-row CT angiography as a preoperative evaluation for spinal arteriovenous fistulae. Neurosurg Rev 30(4):321–326, discussion 327
Yamaguchi S, Nagayama T, Eguchi K, Takeda M, Arita K, Kurisu K (2010) Accuracy and pitfalls of multidetector-row computed tomography in detecting spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg Spine 12(3):243–248
Zampakis P, Santosh C, Taylor W, Teasdale E (2006) The role of non-invasive computed tomography in patients with suspected dural fistulas with spinal drainage. Neurosurgery 58(4):686–694, discussion 686–694
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comments
Peter Willems, Leiden, The Netherlands
Arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) may be challenging lesions to diagnose. Their key finding is the early opacification of veins after contrast injection, which requires time-resolved imaging. The gold standard for this is catheter-based angiography (CA). Unfortunately, CA is time-consuming, requires trained personnel, and is associated with the procedural risks of an intra-arterial catheterization. The development of another modality without these downsides would be of value, even if it would not replace catheter angiography as the gold standard. For this, one would need to be aware of the diagnostic value of such a new modality to allow decision making based on its results. In cranial lesions, both time-resolved MRA (trMRA) and time-resolved CTA (4D-CTA) have been shown to reveal fistulas and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) and their diagnostic value is currently under investigation. However, this report is the first to demonstrate an attempt to use 4D-CTA in spinal lesions. This shift of attention from cranial to spinal is not a trivial one. The CT scanner in this report only covers 16 cm per study, which is sufficient for the entire cranium but not for the entire spinal column. Furthermore, issues arise with regard to contrast bolus timing, patient positioning, and patient movement. Finally, spinal fistulas and the vessels involved are often much smaller than their cranial counterparts. Consequently, the authors are to be commended with the successful diagnosis of a small number of spinal arteriovenous shunting lesions, using their novel protocols. On the other hand, it is important to be aware that these results do not imply that any and every shunt will be diagnosed with 4D-CTA. Further (prospective) research will be necessary to determine the true diagnostic value of this modality. Those results would allow us to determine when 4D-CTA, rather than CA, is indicated and what the consequences should be of its findings.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, S., Takeda, M., Mitsuhara, T. et al. Application of 4D-CTA using 320-row area detector computed tomography on spinal arteriovenous fistulae: initial experience. Neurosurg Rev 36, 289–296 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-012-0440-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-012-0440-z