Abstract
Introduction: Although anticoagulation (AC) reduces the risk of a fatal outcome or severe disability in patients with cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis (CVST), prognosis of severe cases is still difficult to predict. The authors studied the clinical course of patients with CVST who died despite AC therapy to look for clinical features that might explain the lethal course of these patients.
Materials and Methods: Retrospective analysis of a series of 79 consecutive patients with CVST who were treated with a standard regimen of dose-adjusted iv heparin. Case histories of patients with a fatal outcome are presented.
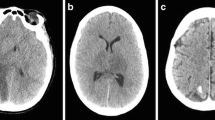
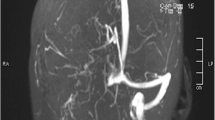
Results: The authors identified eight patients with a fatal outcome. All patients were stuporous or comatose at the start of AC, and four patients showed markedly delayed intracranial circulation times, indicating extensive venous thrombosis. Two patients improved, but deteriorated secondarily after reduction or discontinuation of AC. Sufficient activated partial thromboplastin time levels were reached only after a delay in three patients, and critical deterioration occurred in two of them during this time.
Conclusion: Although inadequate AC may have contributed to the fatal outcome, some patients with extensive venous thrombosis who are stuporous or comatose at the start of AC may carry an increased risk of death, despite heparin therapy. More aggressive treatment approaches, such as endovascular thrombolysis, may be needed for this subgroup of patients with CVST.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bousser MG, Chiras J, Bories J, Castaigne P. Cerebral venous thrombosis-a review of 38 cases. Stroke 1985;16:199–213.
Einhäupl KM, Villringer A, Haberl RL. Clinical spectrum of sinus venous thrombosis. in:. Cerebral Sinus Thrombosis: Experimental and Clinical Aspects (Einhäupl KM, Kempski O, Baethmann A, eds), Plenum Press, New York, 1990, pp. 149–155.
Bousser MG. Cerebral venous thrombosis. Nothing, heparin, or local thrombolysis? Stroke 1999;30:481–483.
Einhäupl KM, Villringer A, Meister W, et al. Heparin treatment in sinus venous thrombosis. Lancet 1991;338:597–600.
de Bruijn SFTM, Stam J, for the Cerebral Venous Sinus Study Group. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of anticoagulant treatment with low-molecular-weight heparin for cerebral sinus thrombosis. Stroke 1999;30:484–488.
Mehraein S, Schmidtke K, Villringer A, Valdueza JM, Masuhr F. Heparin treatment in cerebral sinus and venous thrombosis: patients at risk of fatal outcome. Cerebrovasc Dis 2003;15:17–21.
de Bruijn SFTM, Stam J, for the Cerebral Venous Sinus Study Group. Clinical features and prognostic factors of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in a prospective series of 59 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;70:105–108.
Brucker AB, Vollert-Rogenhofer H, Wagner M, et al. Heparin treatment in acute cerebral sinus venous thrombosis: a retrospective clinical and MR analysis of 42 cases. Cerebrovasc Dis 1998;8:331–337.
Canhao P, Falcao F, Ferro JM. Thrombolytics for cerebral sinus thrombosis. A systematic review. Cerebrovasc Dis 2003;15:159–166.
Kim SY, Suh JH. Direct endovascular thrombolytic therapy for dural sinus thrombosis: infusion of alteplase. Am J Neuroradiol 1997;18:639–645.
Frey JL, Muro GJ, McDougall CG, Dean BL, Jahnke HK. Cerebral venous thrombosis: combined intrathrombus rtPA and intravenous heparin. Stroke 1999;30:489–494.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masuhr, F., Mehraein, S. Cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis. Neurocrit Care 1, 355–361 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/NCC:1:3:355
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/NCC:1:3:355