Abstract
Introduction
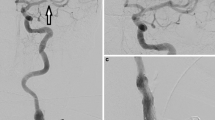
Carotid dissection is a less common but important cause of acute ischemic stroke, which has specific treatment implications.
Case record
We describe the case of a patient with acute, fluctuating neurological symptoms found to be caused by carotid dissection who underwent endovascular stent-supported angioplasty of this lesion with good outcome.
Discussion
Pros and cons of the various treatment options encountered in this case including intravenous thrombolysis, angioplasty and stenting, and antithrombotic therapy are discussed.
Conclusion
Endovascular treatment of carotid dissection in acute stroke can be performed safely. Treatment must ultimately be individualized to each specific case.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brott T, Adams HP Jr., Olinger CP, et al.. Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: a clinical examination scale. Stroke 1989; 20:864–870.
The National Institutes of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. NEJM 1995;333:1581–1587.
Barber PA, Zhang J, Demchuk AM, Hill MD, Buchan AM. Why are stroke patients excluded from TPA therapy? An analysis of patient eligibility Neurology 2001;56:1015–1020.
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993;24:35–41.
Chaves C, Estol C, Esnaola MM, et al Spontaneous intracranial internal carotid artery dissection: report of 10 patients. Arch Neurol 2002;59:977–981.
Ezzeddine MA, Lev MH, McDonald CT, et al. CT angiography with whole brain perfused blood volume imaging: added clinical value in the asessment of acute stroke. Stroke 2002;33:959–966
Lev MH, Farkas J, Rodriguez VR, et al. CT angiography in the rapid triage of patients with hyperacute stroke to intraarterial thrombolysis: accuracy in the detection of large vessel thrombus. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2001;25:520–528.
Hjort N, Butcher K., Davis SM, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging criteria for thrombolysis in acute cerebral infarct. Stroke 2005; 2:388–397.
Amar AP, Larsen DW, Teitelbaum GP. Percutaneous carotid angioplasty and stenting with the use of gadolinium in lieu of iodinated contrast medium: technical case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 2001;49:1262–1265.
Chernyshev OY, Garami Z, Calleja S, et al. Yield and accuracy of urgent combined carotid/transcranial ultrasound testing in acute cerebral ischemia Stroke 2005;36:32–37.
Arboix A, Garcia Eroles L, Massons JB, Oliveres M, Pujades R, Targa C. Atrial fibrillation and stroke: clinical presentation of cardioembolic versus atherothrombotic infarction. Int J Cardiol 2000;73:33–42.
Fisher CM, Ojemann RG, Roberson GH. Spontaneous dissection of cervicocerebral arteries. Can J Neurol Sci 1978;5:9–19.
Shih LC, Saver JL, Alger JR, et al., Perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging thresholds identifying core, irreversibly infarcted tissue. Stroke 2003;34:1425–1430.
Lyrer P, Engelter S, Lyrer P, Engelter S. Antithrombotic drugs for carotid artery dissection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000;(4) CD000255.
Kim SH, Qureshi AI, Levy EI, Hanel RA, Siddiqui AM, Hopkins LN. Emergency stent placement for symptomatic acute carotid artery occlusion after endarterectomy. Case report J Neurosurg 2004;101:151–153.
Beletsky V, Nadareishvili Z, Lynch J, Shuaib A Woolfenden A, Norris JW, Canadian Stroke Consortium. Cervical arterial dissection: time for a therapeutic trial? Stroke 2003;34:2856–3860.
Lennihan L, Mayer SA, Fink ME, et al. Effect of hypervolemic therapy on cerebral blood flow after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke 2000;31:383–391.
Cohen JE, Ben-Hur T, Rajz G, Umansky F, Gomori JM. Endovascular stent-assisted angioplasty in the management of traumatic internal carotid artery dissections. Stroke 2005;36:45–47.
Harker LA, Marzec UM, Kelly AB, et al. Clopidogrel inhibition of stent, graft, and vascular thrombogenesis with antithrombotic enhancement by aspirin in nonhuman primates. Circulation. 1998;98:2461–2469.
Qureshi AI, Luft AR, Sharma M, Guterman LR, Hopkins LN: Prevention and treatment of thromboembolic and ischemic complications associated with endovascular procedures: Part II—Clinical aspects and recommendations. Neurosurgery 2002;46:1360–1376.
Cassar K, Ford I, Greaves M, Bachoo P, Brittenden J. Randomized clinical trial of the antiplatelet effects of aspirin-clopidogrel combination versus aspirin alone after lower limb angioplasty. Br J Surg 2005;92:159–165.
Patti G, Colonna G, Pasceri V, Pepe LL, Montinaro A, Di Sciascio G. Randomized trial of high loading dose of clopidogrel for reduction of periprocedural myocardial infarction in patients undergoing coronary intervention: results from the ARMYDA-2 (Antiplatelet therapy for Reduction of MYocardial Damage during Angioplasty) study. Circulation 2005;111:2099–2106.
The GUSTO IV-ACS investigators. Effect of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor blocker abciximab on outcome in patients with acute coronary syndromes without early coronary revascularization: the GUSTO IV-ACS randomized trial. Lancet. 2001;357:1915–1924.
Furlan A, Higashida R, Wechsler L, et al., for the PROACT Investigators. JAMA 1992;282:2003–2011.
SSYLVIA Study Investigators. Stenting of Symptomatic Atherosclerotic Lesions in the Vertebral or Intracranial Arteries (SSYL-VIA): study results. Stroke 2004;35:1388–1392.
Barnett HJM, Taylor W, Eliasziw M, et al., for the North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators. Benefit of carotid endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic moderate or severe stenosis. NEJM 1998;339:1415–1425.
Jiang WJ, Wang YJ, Du B, et al. Stenting of symptomatic M1 stenosis of middle cerebral artery: an initial experience of 40 patients. Stroke 2004;35:1375–1380.
Kim JK, Ahn JY, Lee BH, et al. Elective stenting for symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis presenting as transient ischaemic deficits or stroke attacks: short term arteriographical and clinical outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2004;75:847–851.
Lee JH, Kwon SU, Lee JH, Suh DC, Kim JS. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis: long-term follow-up. Cerebrovasc Dis 2003;15:90–97.
Suh DC, Kim SJ, Lee DH, et al. Outcome of endovascular treatment in symptomatic intracranial vascular stenosis. Korean J Radiol 2005;6:1–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janjua, N., Qureshi, A.I., Kirmani, J. et al. Stent-supported angioplasty for acute stroke caused by carotid dissection. Neurocrit Care 4, 47–53 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/NCC:4:1:047
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/NCC:4:1:047